Before the stats, You must already know what is Merge sort, Selection Sort, Insertion Sort, Bubble Sort, Quick Sort, Arrays, how to get current time.
What is Stable Sorting ?
A sorting algorithm is said to be stable if and only if two records R and S with the same key and with R appearing before S in the original list, R must appear before S in the sorted list.
If you are going to do a multi pass sorting ( On Different attributes ) you must use a stable sorting.
[tabby title=”Bubble Sort”]
Bubble Sort complexity is
Average : О(n2)
Worst : О(n2)
Best : О(n)
void bubbleSort(int* a, int size) {
bool swapped = true;
int j = 0;
int tmp;
while (swapped) {
swapped = false;
j++;
for (int i = 0; i < size - j; i++) {
if (a[i] > a[i + 1]){
tmp = a[i];
a[i] = a[i + 1];
a[i + 1] = tmp;
swapped = true;
}
}
}
}
Advantages:
-Easy Implementation
-Stable Sorting Algorithm
-In place sorting algorithm
Disadvantages:
-Complexity of O(N^2)
-The majority of O(N^2) algorithms outperform bubble sort
[tabby title=”Selection Sort”]
Selection Sort Complexity is
Average : О(n2)
Worst : О(n2)
Best : О(n2)
void selectionSort(int* a, int size)
{
for (int i = 2; i < size; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j >= 1; j--)
{
if (a[j] < a[j - 1])
{
int temp = a[j - 1];
a[j - 1] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
Advantages:
-Easy Implementation
-In Place Sorting Algorithms
Disadvantages:
-Unstable Sorting Algorithm
-Complexity of O(N^2)
-Some O(N^2) sorting algorithms outperform bubble sort
[/tab_element]
[tab_element title=”Insertion Sort”]
Insertion Sort Complexity is
Average : О(n2)
Worst : О(n2)
Best : О(n)
void insertionSort(int* a, int size)
{
for (int i = 1;i < size;i++)
{
int x = a[i];
int j = i;
while (j > 0 && a[j-1] > a[j])
{
int temporaryVariable=a[j];
a[j] = a[j-1];
a[j-1]=temporaryVariable;
j --;
}
a[j] = x;
}
}
Advantages:
-Easy Implementation
-Stable Sorting Algorithm.
-Outperforms many O(N^2) sorting alogrithms.
-In place sorting algorithm
Disadvantages:
-Complexity of O(N^2)
[tabby title=”Merge Sort”]
Merge Sort complexity is always O(n log(n) ).
void merge(int* a, int first, int middle, int last)
{
int j,i0,i1;
i0 = first;
i1 = middle;
// While there are elements in the left or right runs
for (j = first; j < last; j++) {
// If left run head exists and is <= existing right run head.
if (i0 < middle && (i1 >= last || a[i0] <= a[i1])){
b[j] = a[i0];
i0++;
}
else{
b[j] = a[i1];
i1++;
}
}
}
void split(int* a, int first, int last)
{
if (last - first<2)
return;
int middle = floor((first + last) / 2);
//cout<<first<<" "<<middle<<" "<<last<<endl;
split(a, first, middle);
split(a, middle, last);
merge(a, first, middle, last);
copyArray(a,b, first, last);
}
Advantages:
-Complexity of O(n log(n))
-Stable Sorting Algorithm.
-In-place sorting algorithm
Disadvantages:
-Relatively harder to implement.
-Quick sort usually outperforms merge sort
-Not in place sorting algorithm
[tabby title=”Quick Sort”]
Quick Sort complexity is
Average : О(n log (n))
Worst : О(n2)
Best : О(n log (n))
int partition(int* a, int top, int bottom)
{
int x = a[top];
int i = top - 1;
int j = bottom + 1;
int temp;
do
{
do
{
j--;
}while (x >a[j]);
do
{
i++;
} while (x <a[i]);
if (i < j)
{
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}while (i < j);
return j;
}
void _quickSort(int * a, int top, int bottom)
{
int middle;
if (top < bottom)
{
middle = partition(a, top, bottom);
_quickSort(a, top, middle); // sort first section
_quickSort(a, middle+1, bottom); // sort second section
}
return;
}
void quickSort(int * a, int size)
{
_quickSort(a,0,size);
return;
}
Advantages:
-Complexity of O(n log(n))
-Quick sort is one of the fastest sorting algorithms
Disadvantages:
-Hard to implement.
-Unstable sorting algorithm.
-Not in place sorting algorithm
[tabbyending]
The algorithm is simple : Populate an array with random integers, try the algorithm, get execution time of the algorithm ( How many milliseconds to complete ), populate another array with random integers, try another algorithm, get execution time, repeat with larger arrays with different algorithms
Code :
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <ctime>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <math.h>
/*
* Visit : http://www.titrias.com/ultimate-sorting-algorithms-comparison/ for a complete comparison
*/
using namespace std;
int* b;
bool odd;
bool enablePrinting=false;
struct SortingAlgorithm{
string name;
long long time;
void (*algorithm)(int*,int);
};
//Selection Sort
void selectionSort(int* a, int size)
{
for (int i = 2; i < size; i++)
{
for (int j = i; j >= 1; j--)
{
if (a[j] < a[j - 1])
{
int temp = a[j - 1];
a[j - 1] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}
}
}
/////////////////////////////
//Insertion Sort
void insertionSort(int* a, int size)
{
for (int i = 1;i < size;i++)
{
int x = a[i];
int j = i;
while (j > 0 && a[j-1] > a[j])
{
int temporaryVariable=a[j];
a[j] = a[j-1];
a[j-1]=temporaryVariable;
j --;
}
a[j] = x;
}
}
/////////////////////////////
//Merge Sort
void merge(int* a, int first, int middle, int last)
{
int j,i0,i1;
i0 = first;
i1 = middle;
// While there are elements in the left or right runs
for (j = first; j < last; j++) {
// If left run head exists and is <= existing right run head.
if (i0 < middle && (i1 >= last || a[i0] <= a[i1])){
b[j] = a[i0];
i0++;
}
else{
b[j] = a[i1];
i1++;
}
}
}
///////////////////////////////
//Bubble Sort
void bubbleSort(int* a, int size) {
bool swapped = true;
int j = 0;
int tmp;
while (swapped) {
swapped = false;
j++;
for (int i = 0; i < size - j; i++) {
if (a[i] > a[i + 1]){
tmp = a[i];
a[i] = a[i + 1];
a[i + 1] = tmp;
swapped = true;
}
}
}
}
//////////////////////////////////
//Quick Sort
int partition(int* a, int top, int bottom)
{
int x = a[top];
int i = top - 1;
int j = bottom + 1;
int temp;
do
{
do
{
j--;
}while (x >a[j]);
do
{
i++;
} while (x <a[i]);
if (i < j)
{
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[j];
a[j] = temp;
}
}while (i < j);
return j;
}
void _quickSort(int * a, int top, int bottom)
{
int middle;
if (top < bottom)
{
middle = partition(a, top, bottom);
_quickSort(a, top, middle);
_quickSort(a, middle+1, bottom);
}
return;
}
void quickSort(int * a, int size)
{
_quickSort(a,0,size);
return;
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void copyArray(int* a,int* b, int first, int last)
{
for(int k = first; k < last; k++)
a[k] = b[k];
}
void split(int* a, int first, int last)
{
if (last - first<2)
return;
int middle = floor((first + last) / 2);
//cout<<first<<" "<<middle<<" "<<last<<endl;
split(a, first, middle);
split(a, middle, last);
merge(a, first, middle, last);
copyArray(a,b, first, last);
}
void mergeSort(int *a, int size){
split(a,0,size);
}
/////////////////////////////
int* populateArray(int size)
{
b=new int[size];
int* a = new int[size];
for (int i = 0;i < size;i++)
{
a[i] = rand() % 50000;
b[i]=-1;
}
return a;
}
void printArray(int* a,int size)
{
for (int i = 0;i < size;i++)
{
if(enablePrinting)
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
if(enablePrinting)
cout<<endl;
}
long long now()
{
//LINUX ONLY.
struct timeval timeNow;
gettimeofday(&timeNow, NULL);
return (timeNow.tv_sec * 1000000 + timeNow.tv_usec);
}
int diff(timespec end, timespec start)
{
timespec temp;
if ((end.tv_nsec-start.tv_nsec)<0) {
temp.tv_sec = end.tv_sec-start.tv_sec-1;
temp.tv_nsec = 1000000000+end.tv_nsec-start.tv_nsec;
} else {
temp.tv_sec = end.tv_sec-start.tv_sec;
temp.tv_nsec = end.tv_nsec-start.tv_nsec;
}
return temp.tv_sec;
}
SortingAlgorithm createSortingAlgorithm(string name,void (* f)(int*,int)){
SortingAlgorithm sortingAlgorithm;
sortingAlgorithm.name=name;
sortingAlgorithm.algorithm=f;
sortingAlgorithm.time=0;
return sortingAlgorithm;
}
int main()
{
int numberOfAlgorithms=5;
SortingAlgorithm* sortingAlgorithms=new SortingAlgorithm[numberOfAlgorithms];
sortingAlgorithms[0]=createSortingAlgorithm("Bubble",&bubbleSort);
sortingAlgorithms[1]=createSortingAlgorithm("Selection",&selectionSort);
sortingAlgorithms[2]=createSortingAlgorithm("Insertion",&insertionSort);
sortingAlgorithms[3]=createSortingAlgorithm("Merge",&mergeSort);
sortingAlgorithms[4]=createSortingAlgorithm("Quick",&quickSort);
int sizes[10] ={10000, 20000, 30000, 40000, 50000, 60000, 70000, 80000, 90000, 100000};
long long start, end;
ofstream CFile ("comparison.csv");
CFile<<"SIZE;";
for( int k =0 ;k<numberOfAlgorithms;k++){
CFile<<sortingAlgorithms[k].name<<";";
}
CFile<<endl;
for (int i = 0;i < 10;i++)
{
srand(rand());
int size = sizes[i];
for (int j = 0;j < 1;j++)
{
for( int k =0 ;k<numberOfAlgorithms;k++){
int* a = populateArray(size);
start = now();
sortingAlgorithms[k].algorithm(a, size);
end = now();
sortingAlgorithms[k].time+= end- start;
}
}
CFile<<size<<";";
for( int k =0 ;k<numberOfAlgorithms;k++){
cout << sortingAlgorithms[k].name<<" " << size << " : " << sortingAlgorithms[k].time << endl;
CFile<<sortingAlgorithms[k].time<<";";
sortingAlgorithms[k].time=0;
}
CFile<<endl;
}
return 0 ;
}
N is the number of integers in an unsorted array.
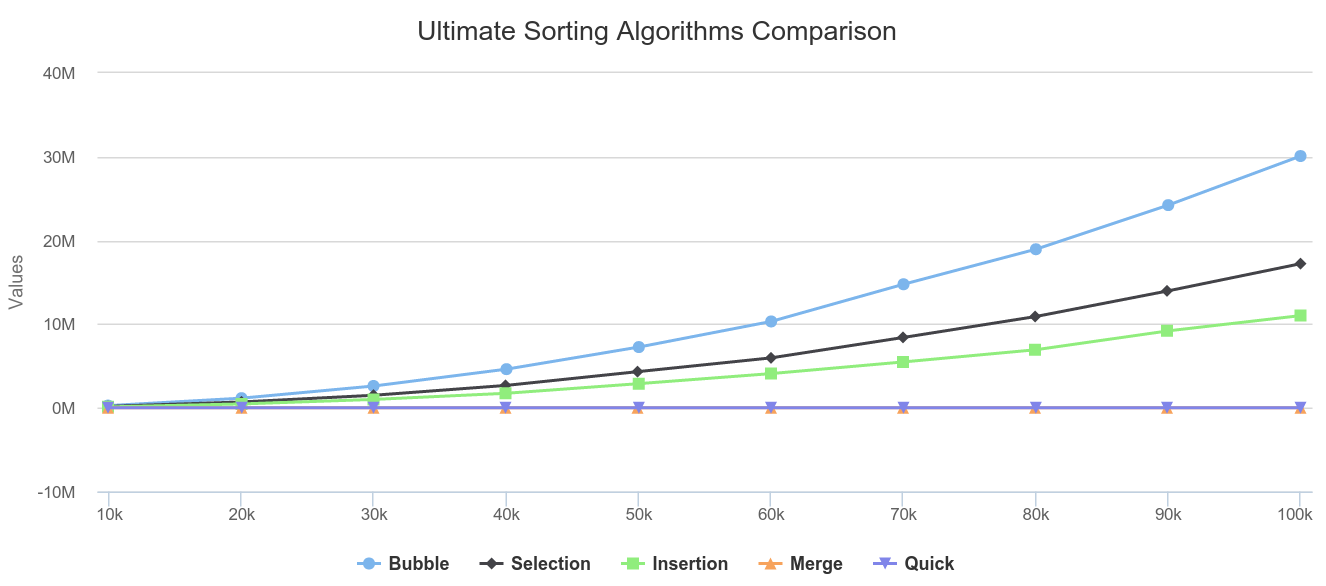
| SIZE | Bubble | Selection | Insertion | Merge | Quick |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10000 | 268337 | 172188 | 112927 | 1354 | 1251 |
| 20000 | 1153151 | 698674 | 461337 | 3266 | 2167 |
| 30000 | 2608569 | 1500900 | 1003081 | 5153 | 3622 |
| 40000 | 4616671 | 2678436 | 1736024 | 7259 | 5162 |
| 50000 | 7256359 | 4331037 | 2885653 | 8673 | 6439 |
| 60000 | 10316054 | 5965544 | 4086762 | 13304 | 8664 |
| 70000 | 14760440 | 8406086 | 5481356 | 13352 | 9916 |
| 80000 | 18946896 | 10907601 | 6936996 | 13933 | 11119 |
| 90000 | 24215815 | 13973373 | 9193457 | 16549 | 12253 |
| 100000 | 30075729 | 17215122 | 11014322 | 18453 | 12940 |
NOTE : If the graphs didn’t show up, Just refresh the page.











0 Comments
Trackbacks/Pingbacks